
To evaluate the effectiveness of a marketing campaign, the business could calculate the incremental revenue. One way to ensure that such an action would result in a profit is through the calculation of incremental revenue. Before accepting the special order, the business contribution margin must first determine if the additional revenue is just enough to produce a profit. They are always composed of variable costs, which are the costs that fluctuate with production volume.
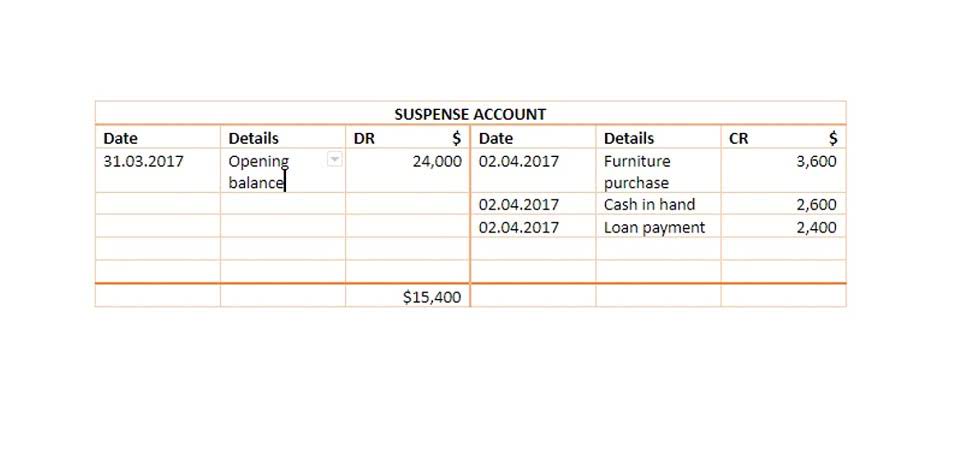
Alternatively, once incremental costs exceed incremental revenue for a unit, the company takes a loss for each item produced. Therefore, knowing the incremental cost of additional units of production and comparing it to the selling price of these goods assists in meeting profit goals. Incremental cost analysis is often used to analyze business segments to determine their profitability.
Incremental revenue is the additional revenue that a company generates from new products, services, or initiatives. To calculate incremental revenue, you first need to identify the total revenue for the period in question. Then, you need to subtract the revenue generated from existing products, services, and initiatives.


Incremental cost is calculated by analyzing the additional expenses involved in the production process, such as raw materials, for one additional unit of production. Understanding incremental costs can help companies boost production efficiency and profitability. From a managerial perspective, incremental costing provides valuable insights into the cost-effectiveness of different options. It helps businesses identify the additional costs incurred and the corresponding benefits gained by choosing one option over another. This analysis enables decision-makers to allocate resources efficiently and optimize their financial outcomes.
Learn more about the standards we follow in producing Accurate, Unbiased and Researched Content in our editorial policy.
This is usually done by comparing the incremental revenue with the incremental cost. Assumptions form the foundation of any analysis, and it is crucial to make reasonable and justifiable assumptions. These assumptions provide a framework for our calculations and help us make informed decisions. However, it is essential to recognize that assumptions are simplifications of reality and may introduce uncertainties into our incremental revenue and incremental cost analysis.